Pricing, particularly transaction pricing, plays a crucial role in determining a company’s success. Although many businesses are well-acquainted with transaction price management, a significant number overlook the specific components that influence the ultimate price of their products, often concentrating solely on List Price or Invoice Price. By conducting a price waterfall analysis, companies can identify potentially hidden areas of price leakage that have unknowingly been negatively impacting their bottom line.
What is a Price Waterfall Analysis?
A price waterfall analysis is a method used in business and pricing strategy to break down and analyze the components that contribute to the overall price of a product or service. It involves examining the various cost elements, markups, discounts, and other factors that influence the final price. The analysis typically follows the sequential flow of how the price changes at each stage of the sales process, creating a visual representation, or “waterfall” of pricing components. This helps businesses understand the factors impacting their pricing structure and can guide decision-making to improve profitability and competitiveness.
Presented below is an illustration exemplifying a standard Price Waterfall:
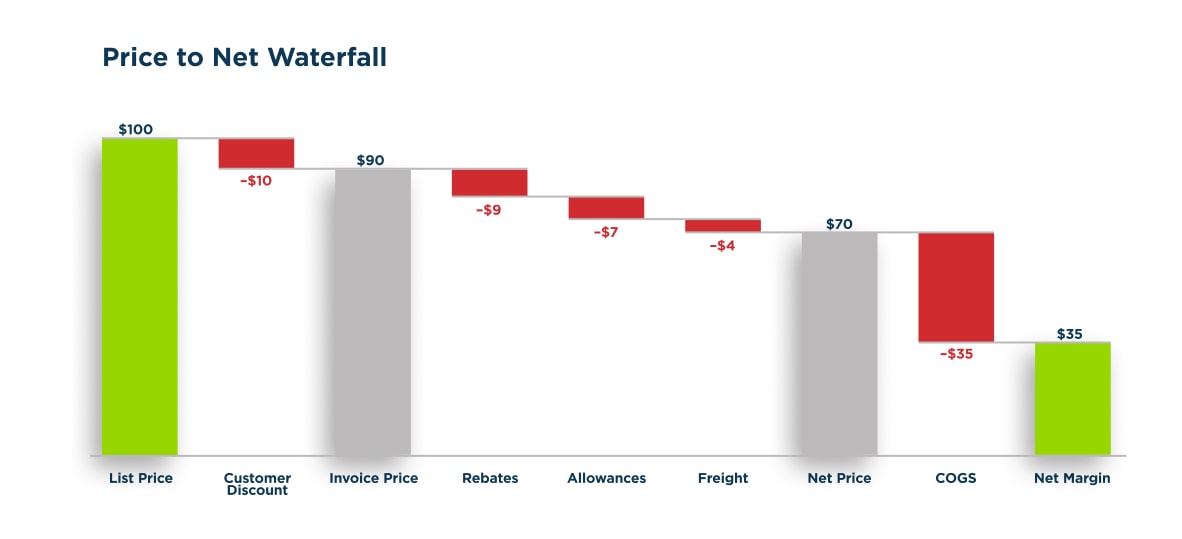
Why Do Price Waterfalls Matter?
The Price Waterfall matters in revenue management because it provides a useful way to leverage your company’s existing sales transaction data to identify margin improvement opportunities. Each leakage or deduction represents an area where adjustments can be made, such as:
- Determine which discounts and allowances are suboptimal and need to be revised or replaced
- Determine which discounts and allowances customers care about most and can influence their buying decisions
- Quantify the financial impact of changing deductions
- Segment customers within a channel
- Determine which products and services are least profitable
- Determine the mix of products and services to sell to customers to augment margin
- Determine which channels provide the most significant opportunity to grow margin
- Determine how actual prices have evolved due to changes in deductions
Being able to execute the above activities is essential as addressing these issues brings an organization closer to capitalizing upon opportunities to grow the bottom line.
Important Note on Leakages/Deductions:
Understanding deductions involves categorizing them into two groups: investments and leakages. Well-executed discounts, allowances, and rebates contribute positively, while poorly executed deductions result in value destruction. Consider whether deductions are contractual or discretionary and whether they are conditional or unconditional. To ensure deductions are investments, focus on appropriate performance targets, gradually increase conditional deductions, and incorporate conditionality requirements in contracts.
How To Use a Price Waterfall to Create a Pricing Strategy?
Creating a pricing strategy using the waterfall pricing method involves a systematic approach to consider various factors and optimize pricing for maximum profitability. Here are steps to guide you in developing a pricing strategy following the waterfall pricing method:
- Understand Your Costs: Start by understanding the costs associated with your product or service. This includes production costs, distribution costs, and any other relevant expenses.
- Identify Value Drivers: Determine the key value drivers that influence your customers’ purchasing decisions. Understand what aspects of your product or service are most valuable to them.
- Define Pricing Objectives: Clearly outline your pricing objectives. Are you aiming for market share, profitability, or a balance between the two? Your objectives will shape your pricing strategy.
- Set a Reference Price: Establish a reference price, often termed the “List Price” or “Base Price.” This is the starting point for your pricing strategy.
- Determine Customer-Specific Discounts: Consider customer-specific discounts based on factors such as the customer’s size, loyalty, or purchasing volume.
- Calculate Invoice Price: Calculate the Invoice Price by subtracting customer-specific discounts from the reference price. This is the price customers are billed.

